Cyber Criminals Leave Stolen Phishing Credentials in Plain Sight says Check Point Research

By Lotem Finkelsteen, Head of Threat Intelligence at Check Point Software
Cyber-crime is a complex landscape, but when it comes to actually launching cyber-attacks, there are three main techniques that criminals have relied on for decades to help them get around organizations’ defenses and into their networks: phishing, credentials theft and business email compromise. According to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigation Report, these ‘big three’ are the cause over two-thirds (67%) of all successful data breaches globally.
Check Point Research recently joined forces with Otorio to analyze and take a deep dive into a large scale phishing campaign that targeted thousands of global organizations, revealing the campaign’s overall infection chain, infrastructure and how the emails were distributed.
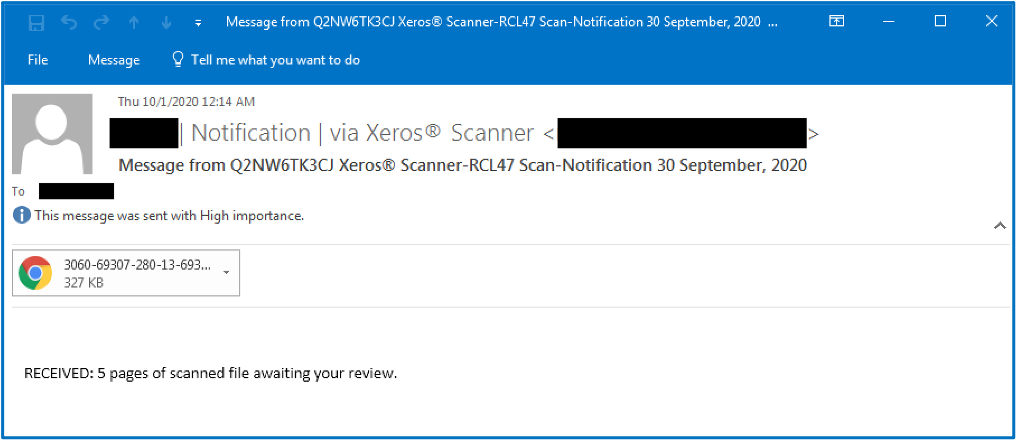
In August 2020, attackers initiated a phishing campaign with emails that masqueraded as Xerox scan notifications, prompting users to open a malicious HTML attachment. While this infection chain may sound simple, it successfully bypassed Microsoft Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) filtering and stole over a thousand corporate employees’ credentials.
Interestingly, due to a simple mistake in their attack chain, the attackers behind the phishing campaign exposed the credentials they had stolen to the public Internet, across dozens of drop-zone servers used by the attackers. With a simple Google search, anyone could have found the password to one of the compromised, stolen email addresses: a gift to every opportunistic attacker.

“We tend to believe that when someone steals our passwords, the worst case scenario is that the information will be used by hackers who exchange them through the dark net. Not in this case. Here, the entire public had access to the information stolen. The strategy of the attackers was to store stolen information on a specific webpage that they created. That way, after the phishing campaigns ran for a certain time, the attackers can scan the compromised servers for the respective webpages, collecting credentials to steal. The attackers didn’t think that if they are able to scan the internet for those pages — Google can too. This was a clear operation security failure for the attackers.”
Infection Chain
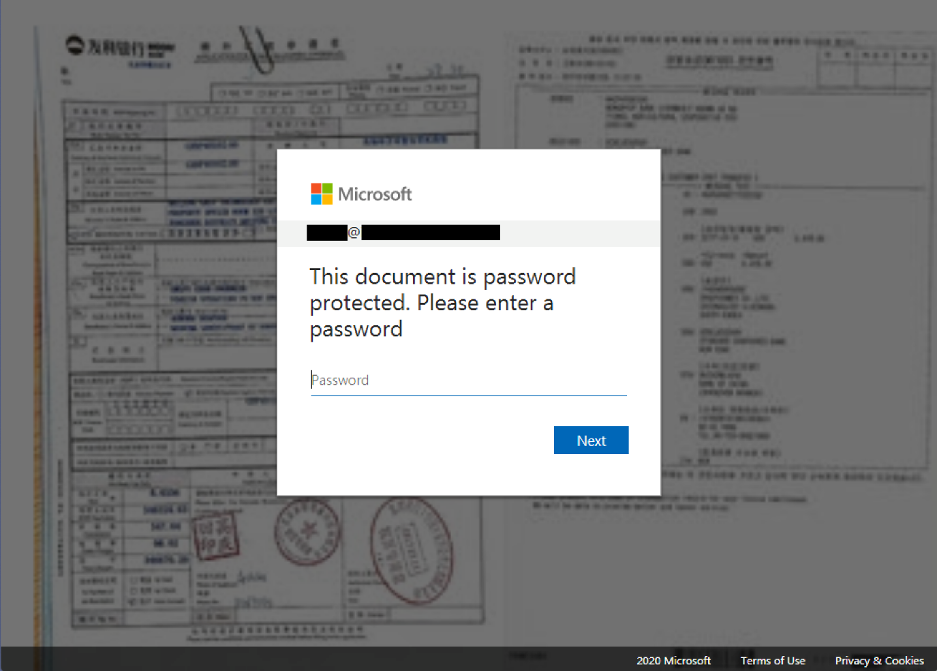
The initial attack started with one of several phishing email templates. The attacker would send an email imitating a Xerox (or Xeros) scan notification with the target’s first name or company title in the subject line. Once the victim double-clicked the attached HTML file, the default system browser displayed a blurred image with a preconfigured email within the document
Throughout the campaign several other phishing page variants were used, but the blurred background image remained the same. After the HTML file was launched, a JavaScript code would then run in the background of the document. The code was responsible for simple password checks, sending the data to the attackers’ drop-zone server, and redirecting the user to a legitimate Office 365 login page.
Throughout the campaign, the code was continuously polished and refined, with the attackers creating a more realistic experience so the victims were less likely to have their suspicions aroused, and more likely to provide their login credentials.
By using simple techniques, the attackers were also successful in evading detection by most Anti-Virus vendors, as can be seen from the following detection rates from the latest iteration of the campaign
Targeted Organizations
We found that once the users’ information was sent to the drop-zone servers, the data was saved in a publicly visible file that was indexable by Google. This allowed anyone access to the stolen email address credentials with a simple Google search. The public availability of this data allowed us to create a breakdown of the victims according to their industry (based on a subset of ~500 stolen credentials). Although there was a wide distribution of targeted industries, there appears to be a special interest in Energy and Construction companies.
We discovered a phishing email from May 2020 that perfectly matched the TTP’s described above. It also used the same JavaScript encoding that was used by this campaign in August. In this older scenario, the script redirected the user to another variant of an Office 365 phishing page that was not entirely encoded within the initial HTML file. Google search engine algorithm naturally indexes the internet, and that is what makes it the most popular search engine ever invented. Thanks to its powerful algorithm, it also capable of indexing the hackers pages where they temporarily store the stolen credentials. We informed Google for them indexing the hackers’ failures and victims now can use Google search capabilities to look for their stolen credentials and change their passwords accordingly.
Conclusion
Our analysis of this campaign highlights the efforts that attackers will make to conceal their malicious intentions, bypass security filtering and trick users. To protect yourself against this type of attack, be suspicious of any email or communication from a familiar brand or organization that asks you to click on a link or open an attached document. Here are some practical tips to help keep your data safe:
- Beware of lookalike domains, spelling errors in emails or websites, and unfamiliar email senders.
- Be cautious with files received via email from unknown senders, especially if they prompt for a certain action you would not usually do.
- Ensure you are ordering goods from an authentic source. One way to do this is to NOT click on promotional links in emails, and instead, Google your desired retailer and click the link from the Google results page.
- Beware of “special” offers that don’t appear to be reliable or trustworthy purchase opportunities.
- Make sure you do not reuse passwords between different applications and accounts.
Organizations should prevent zero-day attacks with an end-to-end cyber architecture, to block deceptive phishing sites and provide alerts on password reuse in real time. Check Point Infinity is effective because it combines two key ingredients: full convergence across all attack surfaces and all attack vectors, and advanced prevention that can tackle the most sophisticated zero-day phishing and account takeover attacks.



